Smile Transformation: Prosthodontic & Cosmetic Dentistry Blog

If you’ve been experiencing ongoing dental issues that alter your ability to chew, speak, or smile confidently, you might be a candidate for full mouth reconstruction. Unlike cosmetic dentistry, which focuses on aesthetics, full mouth reconstruction combines restorative and functional treatments to rebuild your smile. Here are the top signs it might be right for you. […]
The post Top Signs You Might Be a Candidate for Full Mouth Reconstruction appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

Dental implants are a tried and true method of replacing missing teeth, offering durability and the closest alternative to natural teeth. However, the procedure does require surgery and a period of recovery. It’s important to understand what recovery entails to feel confident and comfortable about your road to a lasting, complete smile. Here’s a detailed timeline […]
The post The Recovery Process After Dental Implant Surgery: Timeline and Tips appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

If you’re getting a dental bridge to restore your smile aesthetic and function, a little pre-planning for recovery can go a long way. Stock up on the right foods for the days and weeks following the procedure, as what you eat is critical in maintaining the integrity of your dental bridge and promoting healing. Here’s a guide […]
The post Foods to Eat and Avoid After Getting Your Dental Bridge appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

If you need a dental crown for a damaged or decayed tooth, you might wonder, “Do dental crowns hurt?” The good news is that modern dentistry has made getting a dental crown much more comfortable than ever before. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect during and after the procedure. Dr. Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD, is […]
The post Do Dental Crowns Hurt? What to Expect During and After the Procedure appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

The holiday season is the perfect time to consider enhancing your smile, especially with all the festivities and merriment. If you’re not satisfied with the appearance of your smile, composite veneers are a quick, effective way to get a beautiful, natural-looking smile just in time for the holidays. Here’s why composite veneers are trending for holiday smile […]
The post Top Reasons Composite Veneers Are Trending for Holiday Smile Transformations appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

The new year is a perfect time for a fresh start, and what better way to begin than with a brighter, whiter smile? You may have used whitening toothpaste or at-home kits before, but nothing compares to professional teeth whitening. Here’s why an in-office whitening is a top choice for revamping your smile in the new […]
The post Smile Bright in The New Year: Benefits of Professional Teeth Whitening appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

Dental bonding is a popular and effective cosmetic treatment that can address a variety of dental issues. Whether you’re looking to improve the appearance of your smile or fix minor dental problems, dental bonding can offer a quick, non-invasive solution. The procedure involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the affected area, which can restore the tooth’s […]
The post Common Issues Dental Bonding Can Fix appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.
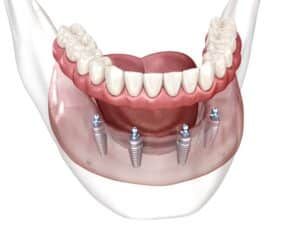
When it comes to restoring your smile after tooth loss, there are several options available. However, traditional dentures and All-on-4 implants are two of the most common. Each solution offers distinct benefits and drawbacks. Understanding their differences can help you determine which option may be best suited for your dental needs. Understanding Traditional Dentures Conventional dentures are removable […]
The post All-on-4 vs. Traditional Dentures appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

Sports mouthguards aren’t just for pro athletes. Active people need extra mouth protection during sports, even if they spend most of their time behind a desk. Dr. Louisa Gallegos prioritizes protecting your smile from preventable damage. A dentist since 1983, Dr. Gallegos has extensive experience helping her patients safeguard their oral health. One key way to protect […]
The post Who Needs to Wear a Sports Mouthguard? appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.

More than 22% of people experience teeth grinding (bruxism) today. Many are unaware that they do it, while others suddenly learn about the problem due to tooth damage. At her private practice in Denver, CO, Dr. Louisa Gallegos offers compassionate care focusing on restoring your oral health. If you’re worried about the long-term damage bruxism may cause, we’re here to […]
The post Can Bruxism Damage Your Teeth? What You Need to Know appeared first on Louisa Gallegos, DDS, MSD - Prosthodontist.